Survival analysis is used to determine the time it takes for an event of interest to occur. We use survival analysis to study the time until some event of interest occurs.
Survival Analysis is also known as Time to Event analysis
Objective:
The objectives of survival analysis is to analyze patterns of event times, the comparison of distributions of survival times in different desired groups and examining how much some factors affect the risk of an event of interest.
Input:
Survival time can be measured in years, months, days etc.,
The event of interest could be anything of interest. It could be an actual death, a birth, a retirement, along with others.
- We can calculate which treatment has the highest survival probability.
- We can calculate which factor has more impact on patient’s survival.
Survival analysis can also be used to compare time-to-event for multiple groups.
Survival Time: It is usually referred to as an amount of time until when a subject is alive or actively participates in a survey.
There are three main types of events in survival analysis:
1) Relapse: Relapse is defined as a deterioration in the subject’s state of health after a temporary improvement.
2) Progression: Progression is defined as the process of developing or moving gradually towards a more advanced state. It basically means that the health of the subject under observation is improving.
3) Death: Death is defined as the destruction or permanent end of something. In our case, death will be our event of interest.
Kaplan-Meier Estimator
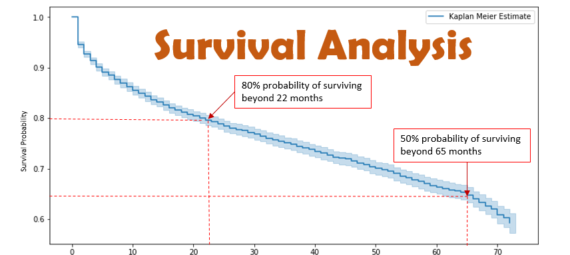
The Kaplan–Meier estimator is a non-parametric statistic used to estimate the survival function (probability of a person surviving) from the lifetime data. In medical research, it is often used to measure the fraction of patients living for a specific time after treatment or diagnosis.
Using Kaplan Meier estimator, we can estimate the probability for each time point.
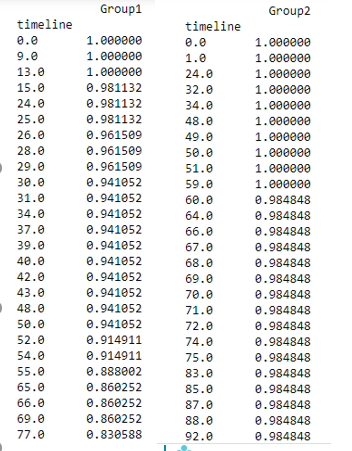
As Survival Analysis can be used for the cohort analysis, to gain insights. Here we can see the estimated probability for each of the group separately as an output.