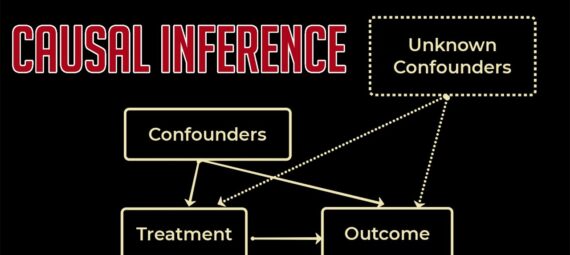
Causal inference is important in healthcare because it allows researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to understand the causal relationships between different factors and health outcomes. This is critical for developing effective interventions, improving patient outcomes, and optimizing healthcare resource allocation.
In healthcare, causal inference is particularly important because many decisions, such as treatment selection and policy decisions, rely on accurate and reliable evidence about the causal relationships between different factors and health outcomes. For example, if a new drug is developed to treat a certain condition, it is important to know whether the drug actually causes an improvement in patient outcomes or if the observed improvement is due to other factors, such as chance or placebo effects.
Causal inference is also important in healthcare because it helps to identify and mitigate sources of bias, such as confounding, selection bias, and measurement bias. These biases can distort the relationship between factors and outcomes, making it difficult to draw accurate conclusions about causality. By using causal inference methods, researchers can adjust for these biases and obtain more reliable estimates of causal effects.
Overall, causal inference is critical for advancing healthcare research and practice, and for improving patient outcomes. By understanding the causal relationships between different factors and health outcomes, researchers and healthcare providers can develop more effective interventions, make better decisions, and ultimately improve the health and well-being of individuals and populations.